Delete Operation
- Trace the basic operations of a (singly) linked list implementation.
- Understand the basic operations of a (singly) linked list well enough to implement them.
Suppose we have a linked list with $n$ elements (nodes) and we want to delete an element at a given index $k$. This means we remove the $k^{th}$ node from the list. After deletion we have $n - 1$ elements:
- The node which was at index $k - 1$ before the deletion will remain at that index after the deletion.
- The nodes at index $k + i$ for $i \in [1, n-1-k ]$ before the deletion will be at index $k+ j$ after the deletion for $j \in [0, n-2-k]$.
For example, we have a linked list with four nodes at indices 0, 1, 2, and 3.
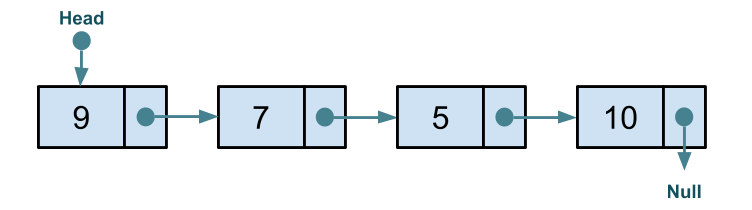
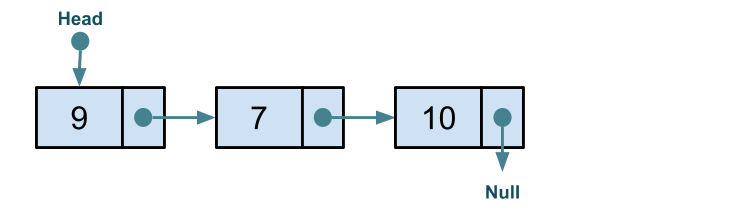
We will delete the node at index 2:
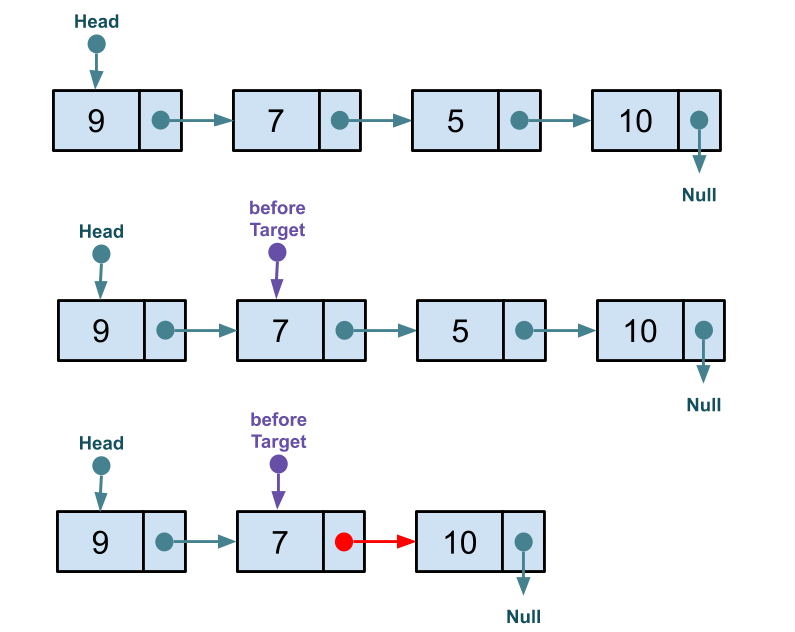
Exercise Complete the implementation of delete which removes a node at the given index.
public void delete(int index) {
// TODO Implement me!
}
Hint: Use the following visualization as guidance.
Solution
public void delete(int index) {
Node<T> beforeTarget = head;
for(int counter = 0; counter < index - 1; counter++) {
beforeTarget = beforeTarget.next;
}
beforeTarget.next = beforeTarget.next.next;
}
Caution: the implementation above fails to account for edge cases and cases where index is invalid!